Broadcasting and streaming are two terms often used interchangeably in media. However, they represent two distinct methods of content delivery. Broadcasting, a traditional method, involves transmitting data to a large audience, like a TV broadcast or radio waves. It’s a one-way communication, with content following a fixed schedule. On the other hand, streaming offers a more engaging and interactive experience, especially live streaming. It allows real-time interaction between the content provider and the audience.
Streaming depends on internet connectivity for smooth and continuous transmission of video content. It eliminates geographical barriers, making content easily accessible to a diverse audience.
This article will explore the key differences between broadcasting and streaming.
📺Broadcasting vs Streaming▶️ Key Differences
Broadcasting and streaming have distinct differences in how they reach audiences. Broadcast TV sends the same content to a larger audience simultaneously. Streaming services deliver content to viewers on a one-to-one basis.
Live broadcasting follows a specific channel’s schedule, while live streams can start anytime. Broadcast television requires separate signals for each program. Streaming platforms allow users to choose content on-demand. Live streaming events often enable audience interaction and engagement.
Broadcasting typically targets a broader audience, while streaming can reach a more targeted audience. Live video solutions for streaming offer more flexibility than traditional broadcasts.
Streaming media can be accessed through various devices and platforms. Both broadcasting and streaming can transmit data for virtual events.
Live broadcasts usually have scheduled content, while live streams can be more spontaneous. Streaming solutions provide more options for creating engaging live content.
📺 What is Broadcasting?
This content delivery method is often used for live events, like a live broadcast on a TV station or radio broadcast. Broadcasting is typically a one-way communication, meaning the audience can receive the content but cannot interact with it in real-time.
The broadcast signal is sent on a fixed schedule and can reach a diverse audience, regardless of geographical barriers. However, the quality of the broadcast depends on the strength of the analog signal and the user’s device.
Broadcasting differs from streaming, which we will discuss later in this article.
How Broadcasting Works
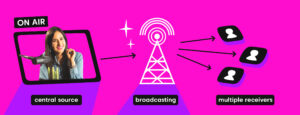
Broadcasting involves sending a signal from a central source, such as a broadcast tower, to multiple receivers. This process is often used in traditional television and radio broadcasting.
The first step in broadcasting is creating content. This could be a live event, such as a sports game or news report, or pre-recorded content, like a TV show or radio program. The content is then sent to a broadcast tower via radio waves.
The broadcast tower plays a significant role in the process. It receives the content and transmits it as a broadcast signal. This signal is sent out in all directions, reaching the TV’s antenna or radio within its range. The signal can be analog, but it is gradually being replaced by digital signals for better video quality.
One of broadcasting’s key features is its one-way communication. The audience can receive and view the content, but they cannot interact with it or influence it. This is different from live streaming, where there is potential for real-time interaction and user engagement.
The Key Features of Broadcasting
Broadcasting is a well-established method of communication that has been around for decades. It has several key characteristics that set it apart from other forms of communication.
Mass communication
Broadcasting is designed to reach a large number of people at the same time. This is done through the use of broadcast signals sent out from a central location, such as a TV station or radio tower. These signals are then picked up by individual receivers, such as TVs or radios, allowing the content to be viewed or listened to by a large audience. This is different from streaming, which is typically a one-to-one communication method.
Real-time transmission
Broadcasting involves the transmission of content in real-time. This means that the content is being broadcast live, as it happens. This is particularly important for live events, such as sports games or news broadcasts, where the audience wants to see the action as it unfolds. In contrast, streaming can involve both live and pre-recorded content.
One-to-many communication
Broadcasting is a one-way communication method. The content is sent out from one source to many receivers. This differs from streaming, which can involve two-way communication, allowing real-time interaction between the content provider and the audience.
Scheduled programming
Broadcasting operates on a fixed schedule. This means that certain programs are broadcast at specific times. This differs from streaming, where the user can choose when to watch or listen to the content.
Wide coverage area
Broadcasting can reach a large geographical area. This is because the broadcast signals can be picked up by any receiver within range of the broadcast tower. This is different from streaming, which requires an internet connection and can be affected by geographical restrictions.
Regulated content
Broadcasting is subject to regulations and standards set by governing bodies. This ensures that the content is suitable for a diverse audience and meets certain quality standards. In contrast, streaming content can be more varied and is sometimes subject to different regulations.
Advertising revenue
Broadcasting relies heavily on advertising revenue. Commercials are often inserted into the broadcast content to generate income. This differs from streaming, where revenue can come from subscription fees or pay-per-view charges.
Advantages of Broadcasting
✔️Broadcasting reaches a wide audience.
✔️It offers a variety of content.
✔️Broadcasting is reliable with a stable connection.
✔️It provides high-quality visuals and audio.
✔️ Broadcasting allows for real-time information sharing.
✔️It has a strong impact due to its mass reach.
Disadvantages of Broadcasting
❌Broadcasting can be expensive to set up.
❌ It requires a lot of resources and manpower.
❌Broadcasting can be subject to censorship.
❌ It may not offer personalized content.
❌ Broadcasting can be affected by bad weather conditions.
❌ It may not reach remote areas effectively.
▶️ What is streaming?
Unlike traditional broadcast TV, streaming media, such as live streaming services, allows for the delivery of audio and video over the Internet.
Live streaming platforms offer a way to broadcast live video and audio to a targeted audience. These platforms provide live-streaming solutions, allowing for engaging live-stream connections during virtual events. Live streaming events can be accessed through various streaming services.
Unlike broadcast television, which sends out separate signals for each channel, streaming sends the same content on a one-to-one basis. This allows more audience interaction, as viewers can engage with the live stream.
Live broadcasts on TV are scheduled content aired on a specific channel. In contrast, live streams can be accessed anytime, anywhere, through a streaming platform. This makes live streaming a more flexible option to reach a larger audience.
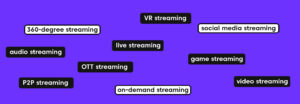
Types of streaming
There are various types of streaming, each with its unique characteristics and uses.
Live Streaming
Live Streaming is a type of streaming in which content is broadcast in real-time. It is often used for events, webinars, and live broadcasts on social media. An example of live streaming is a live TV show or a live-stream concert.
On-Demand Streaming
It allows users to access content whenever they want. Streaming services like Netflix and Hulu commonly use this type of streaming. Users can watch their favorite shows or movies at their convenience, making it a popular choice for streaming media.
Audio Streaming
It involves the transmission of audio files from a server to a user over the Internet. This type of streaming is commonly used by music streaming platforms like Spotify and Apple Music. Users can listen to their favorite songs or podcasts without downloading them.
Video Streaming
Video Streaming is similar to audio streaming, but it involves transmitting video content. Platforms like YouTube and Vimeo use this type of streaming. Users can watch videos without downloading, making it a convenient option for consuming video content.
Game Streaming
Game Streaming allows users to play video games over the internet. Platforms like Twitch and Mixer use this type of streaming. Gamers can play their favorite games and interact with their audience in real-time.
Social Media Streaming
Social Media Streaming is a type of streaming where users can broadcast live videos on social media platforms. This type of streaming is commonly used for live video solutions, engaging live stream connects, and live streaming events.
VR Streaming
Virtual Reality (VR) Streaming involves transmitting VR content over the internet. This type of streaming allows users to experience VR without downloading large files. An example of VR streaming is a virtual tour of a museum or a virtual event.
360-Degree Streaming
360-degree Streaming allows users to view videos in a 360-degree format. This type of streaming is commonly used for virtual tours and immersive videos. Users can view the content from different angles, providing a unique viewing experience.
OTT Streaming
OTT (Over-The-Top) Streaming involves the delivery of film and TV content via the Internet without requiring users to subscribe to a traditional cable or satellite pay-TV service. Examples of OTT streaming services include Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Hulu.
P2P Streaming
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Streaming is a type of streaming where the streamed data is shared directly between users, without going through a central server. This type of streaming is commonly used for sharing large files and live streaming platforms.
Each type of streaming has its benefits and uses. Whether you’re looking to broadcast live video, stream music, or share large files, there’s a streaming solution that’s right for you.
How streaming technology works
Broadcasting and streaming are two distinct methods of transmitting data to a larger audience. The technology behind streaming services is quite fascinating, involving key technologies like CDN, encoder, and others.
CDN
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a network of servers that delivers the live stream to viewers. The CDN ensures that the live video reaches the viewers without delay or buffering.
Encoder
An encoder is a device or software that converts the live video into a format that can be streamed online. The encoder plays a significant role in ensuring the live stream is high quality.
Streaming media server
A streaming media server hosts the live stream and delivers the live video to the CDN.
Streaming platform
Live streaming platforms host the live stream and provide the tools and features necessary for creating an engaging stream.
Streaming services
Live streaming services provide the infrastructure and tools necessary for live streaming events and offer various live streaming solutions, including live video solutions and live streaming platforms.
Streaming software
Live streaming software manages and controls the live stream. It allows for audience interaction and targeted audience engagement.
Streaming devices
Live streaming hardware refers to the equipment used to capture and transmit live video. It includes cameras, microphones, and other devices.
Streaming technology captures live video, encodes it, and then transmits it over the Internet to a specific channel. This allows for one-to-one interaction with the target audience.
The same content can be delivered to separate signals, allowing for a more engaging live stream. This is one of the distinct differences between live broadcasting and live streaming.
Advantages of Live Streaming:
✔️Live streaming allows real-time interaction with the audience.
✔️ It is cost-effective as it eliminates the need for physical venues.
✔️Live streaming has a global reach, enabling viewers from all over the world to participate.
✔️ It provides an opportunity for instant feedback and engagement.
✔️Live streaming can be accessed on smartphones, tablets, and computers.
✔️It offers flexibility as viewers can watch the live stream conveniently.
Disadvantages of Live Streaming:
❌Live streaming is heavily dependent on internet connectivity. Any disruption can affect the viewing experience.
❌It requires certain technical knowledge to set up and manage.
❌ Privacy concerns can arise as live streams are accessible to anyone.
❌ There is a risk of copyright infringement with live streaming.
❌The quality of live streaming can vary based on the viewer’s internet speed.
❌It lacks the personal touch and experience of a physical event.
Use Cases and Applications of Broadcasting and Streaming
Broadcasting and streaming have distinct differences in their use cases and applications.
Broadcasting, such as broadcast TV, is often used for live events, news, and traditional TV programming. Live broadcasting allows a larger audience to view the same content simultaneously on a specific channel. This method is often used for live broadcasts of major events or scheduled content.
On the other hand, streaming is commonly used for movies, TV shows, and user-generated content. Streaming media, such as live streaming services, allows content to be viewed one-to-one. This means that a targeted audience can view the content at any time. Streaming services like live streaming platforms offer live video solutions for a more engaging live stream connection.
There are also hybrid approaches that use both broadcasting and streaming. This approach is often used for live-streaming events that require audience interaction. For example, a virtual event may use a live-streaming platform for the main event and broadcast television for a larger audience. This allows the same content to be transmitted through separate signals, catering to different audience needs.
Industry-specific applications also exist. In education, live streaming solutions connect teachers and students. In sports, live streams broadcast games to a targeted audience.
In entertainment, both broadcasting and streaming deliver content. For example, a concert may be live-streamed for those who paid an admission fee and broadcast for a larger audience.
Whether it’s live streaming or broadcasting, each has its benefits and applications. The choice between the two often depends on the specific needs of the content and the target audience.
Why Prefer Streaming Over Broadcasting?
Streaming offers several advantages over traditional broadcasting.
Here are some key reasons:
Flexibility and On-Demand Access
Streaming services allow viewers to watch content anytime. Users can pause, rewind, or fast-forward through streaming media. This flexibility is not possible with broadcast TV. Streaming platforms offer a wide variety of content. Viewers can choose what they want to watch.
Cost-Effectiveness
Streaming solutions are often more affordable than broadcast television. Many streaming services offer free or low-cost subscriptions. Live streaming platforms can reach a larger audience at a lower cost. Businesses can save money on equipment and transmission costs.
Targeted Content Delivery
Streaming allows content creators to reach their target audience effectively. Live streaming events can be tailored to specific viewer interests. This targeted approach is not possible with traditional broadcasting. Streaming platforms can use data to recommend content to users.
Enhanced Audience Interaction
Live streams offer more opportunities for audience interaction. Viewers can comment and engage with content in real-time, which strengthens the connection between creators and audiences. Live streaming services often include chat features and polls.
Global Reach
Streaming media can reach a global audience instantly. Live video solutions break down geographical barriers. Viewers worldwide can access the same content simultaneously. This global reach is challenging for traditional broadcast TV.
Monetization Options
Streaming platforms offer various monetization options for content creators. These include ads, subscriptions, and pay-per-view models. Live streaming events can charge an admission fee. Creators can earn revenue on a one-to-one basis with viewers.
Conclusion
Adapting to changing media habits is crucial for content creators. Streaming is often the better option for targeted audience engagement. It allows for more interaction and flexibility in content delivery.
Castr offers a comprehensive live-streaming solution for various needs. This platform provides high-quality video, customizable players, and multi-streaming capabilities. Castr also supports features for audience interaction and detailed analytics. It enables content creators to reach viewers on multiple platforms simultaneously.
Try Castr for your next virtual event or live broadcast. Our streaming solutions can help you connect with your audience effectively. Castr makes it easy to create engaging live streams and expand your reach.







